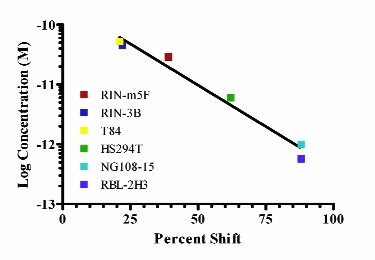
CTB-SAP (Cat. #IT-14) is a conjugate between the cell-binding component of cholera toxin (the B chain) and saporin. CTB binds to GM1 (monosialotetrahexosylganglioside), which is present on the surface of different neurons. It has been suggested to be involved in many problems (besides the most famous in the gut: cholera) of neuronal systems: Parkinson’s, motor neuron degeneration, spinal cord injury, and Alzheimer’s disease among others (see cover article).