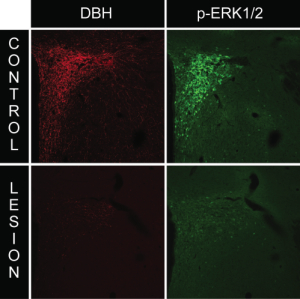
Anti-dopamine beta-hydroxylase-saporin (anti-DBH-SAP, Cat. #IT-03) is a highly specific noradrenergic lesioning agent. It specifically targets rat cells that express dopamine beta-hydroxylase and is also reported to react with mouse protein.1 This vesicular enzyme is exposed to the exterior milieu upon release of noradrenaline and thus allows these cells to be targeted with saporin.
The specificity of Anti-DBH-SAP correlates well with uptake of the antibody when injected intraventricularly. After systemic administration, animals have a massive reduction in plasma norepinephrine levels, indicating efficient targeting and sympathectomy. Unlike other lesioning methods, this molecular lesioning agent assures definitive ablation of the target neurons.
Permanent and selective removal of cerebral noradrenergic innervations provides an important animal model for the study of drug effects, behavior, plasticity of other systems in response to loss, and primary autonomic failure.
1. Harle P, Pongratz G, Albrecht J, Tarner IH, Straub RH (2008) An early sympathetic nervous system influence exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis via CD4+CD25+ cells. Arthritis Rheum 58:2347-2355.
Anti-DBH-SAP References in 2010
Carvalho AF, Reyes AS, Sterling RC, Unterwald E, Van Bockstaele EJ (2010) Contribution of limbic norepinephrine to cannabinoid-induced aversion. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 211(4):479-91.
Coradazzi M, Gulino R, Garozzo S, Leanza G (2010) Selective lesion of the developing central noradrenergic system: short- and long-term effects and reinnervation by noradrenergic-rich tissue grafts. J Neurochem 114(3):761-71.
Emanuel AJ, Ritter S (2010) Hindbrain catecholamine neurons modulate the growth hormone but not the feeding response to ghrelin. Endocrinology 151(7):3237-46.
Itoi K, Sugimoto N (2010) The brainstem noradrenergic systems in stress, anxiety and depression. J Neuroendocrinol 22(5):355-61.
Marques-Lopes J, Pinho D, Albino-Teixeira A, Tavares I (2010) The hyperalgesic effects induced by the injection of angiotensin II into the caudal ventrolateral medulla are mediated by the pontine A5 noradrenergic cell group. Brain Res 1325:41-52.
Milstein JA, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2010) Methylphenidate-induced impulsivity: pharmacological antagonism by beta-adrenoreceptor blockade. J Psychopharmacol 24(3):309-21.
Ng TB, Wong JH, Wang H (2010) Recent progress in research on ribosome inactivating proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11(1):37-53.
Northrop LE, Polston EK, Erskine MS (2010) Noradrenergic nuclei that receive sensory input during mating and project to the ventromedial hypothalamus play a role in mating-induced pseudopregnancy in the female rat. J Neuroendocrinol 22(10):1061-71.
Potes CS, Turek VF, Cole RL, Vu C, Roland BL, Roth JD, Riediger T, Lutz TA (2010) Noradrenergic neurons of the area postrema mediate amylin’s hypophagic action. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299(2):R623-31.
Vianna DML, Carrive P (2010) Cardiovascular and behavioural responses to conditioned fear and restraint are not affected by retrograde lesions of A5 and C1 bulbospinal neurons. Neuroscience 166(4):1210-8.
Worlicek M, Knebel K, Linde HJ, Moleda L, Schölmerich J, Straub RH, Wiest R (2010) Splanchnic sympathectomy prevents translocation and spreading of E coli but not S aureus in liver cirrhosis. Gut 59(8):1127-34.
Anti-DBH-SAP, Cat. #IT-03
available in these sizes: 25 micrograms, 100 micrograms, and 250 micrograms
Kit includes the following controls in equal amounts:
Saporin, Cat. #PR-01
Mouse IgG-SAP, Cat. #IT-18