Selective ablation of striatal striosomes produces the deregulation of dopamine nigrostriatal pathway.
Objective: To increase knowledge in the role of the striosomal projection onto the dopamine neurons of the SNc and its impact on the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway.
Summary: Results highlight the key function of the striosomes for maintenance of the striatal dopamine tone and contribute to the understanding of their involvement in some neurological disorders such as Huntington’s disease.
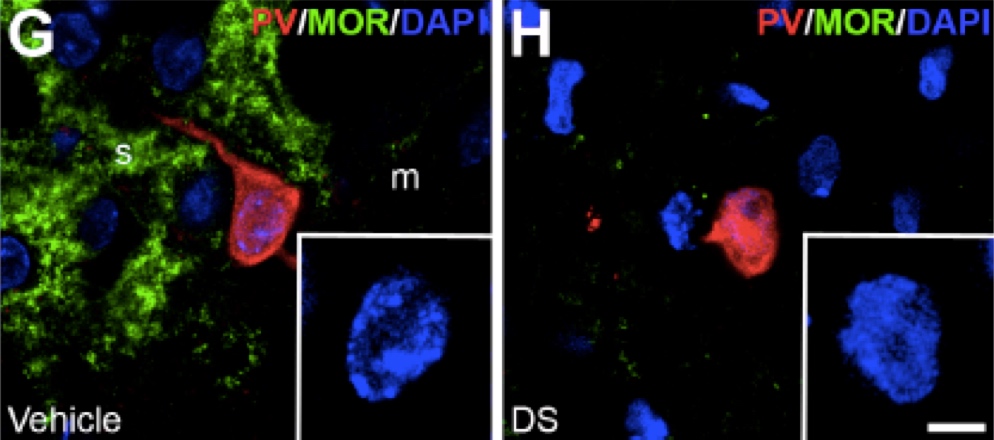
Dose: Unilateral intrastriatal 2-μl injections of Dermorphin-SAP (17 μg/μl in saline) were performed to induce the selective ablation of MOR-expressing neurons in the striosomal compartment.
Shumilov K, Real MÁ, Valderrama-Carvajal A, & Rivera A. (2018). PLoS One, 13 (8):e0203135.
