Hemokinin 1 (HK1) is an 11 amino acid tachykinin produced by the proteolytic processing of a 128 amino acid precursor, preprotachykinin C. This peptide has been shown to bind the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) with the same affinity and potency as substance P. The NK-1R has been implicated in a number of conditions such as hyperalgesia and chronic pain. Hemokinin 1 and the natural ligand for the NK-1R, substance P, have been shown to have equivalent binding to the receptor. The NK-1R is involved with respiratory rhythm, mood disorders, anxiety and stress, and reinforcement. One of the most important roles for NK-1R is in the spinal cord in the transmission of pain signals from peripheral pain receptors to the brain. NK-1R pathway is implicated in the establishment and maintenance of a chronic pain state.
Hemokinin 1-SAP (HK1-SAP) is a chemical conjugate of the hemokinin-1 peptide and the ribosome-inactivating protein, saporin. It eliminates cells expressing the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R). All other cells are left untouched, even when they are the predominant cell type.
HK1-SAP is available individually (Cat. #IT-76) or as a kit (Cat. #KIT-76) which includes HK1-SAP and Blank-SAP (Cat. #IT-21).
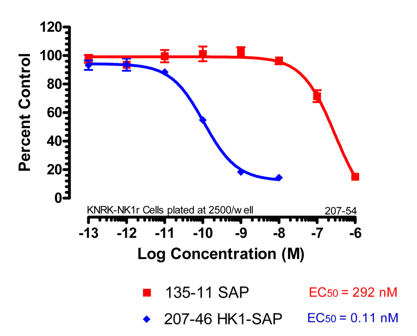
KNRK-NK1R cells were plated at 2500 cells/90 μl/well and incubated overnight. Saporin dilutions were made in cell media and 10 µl was added to each well. The plates were incubated for 72 hours. The plates were developed using a solution of XTT/PMS and read at 450 nm. Cytotoxicity was analyzed by comparing well readings of the treated wells to those of the control wells, expressed as a percentage. The number of viable cells remaining on the day of development is measured via cell metabolism of a colorimetric molecule within the developing reagents. Analysis was performed using Prism software (GraphPad, San Diego).
keywords: hemokinin 1, HK1, Substance P, SP, NK-1R, NK-1 receptor, NK1R, neurokin, saporin, pain, brain, neuroscience


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.